India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): Forging the Arteries of a New Global Order
"Infrastructure is not just about steel and concrete—it's about the connections that empower economies, cultures, and dreams."
The announcement of the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) during the G20 Summit 2023 in New Delhi sent ripples across the geopolitical and economic spheres. Touted as a game-changer in global trade, IMEC is more than a connectivity project—it's a vision that seeks to realign global supply chains, enhance strategic alliances, and offer a counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
This detailed blog explores every aspect of the IMEC—from its conception, structure, stakeholders, technical routes, and economic impact to its geopolitical relevance, technological integration, challenges, and future possibilities. It provides a 360-degree understanding of one of the most ambitious infrastructure visions of the 21st century.
🧭 What is IMEC?
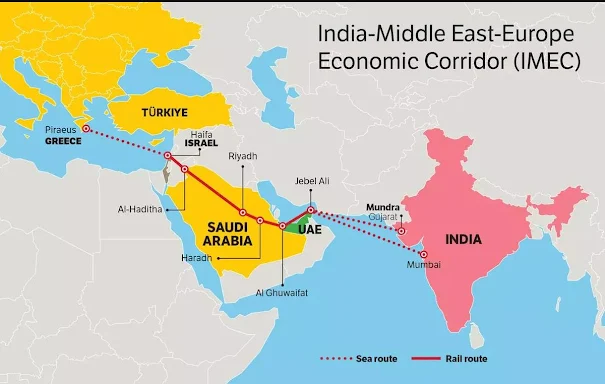
The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is a proposed multimodal transport corridor that connects India with Europe via the Middle East, including the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and then onward to Greece and Europe. IMEC will include:
- Railways
- Shipping networks
- Digital and energy pipelines
The initiative was announced under the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII)—a G7-led initiative designed to fund sustainable infrastructure globally.
🌍 Participating Countries and Partners
- India
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Jordan
- Israel
- European Union (EU) and member states including Greece, Italy, France, and Germany
- United States: Strategic partner and facilitator under PGII
🛤️ Proposed Corridor Route and Infrastructure
1.Eastern Corridor:
- Starts from Mundra/ Mumbai/ Kandla ports in India
- Ships goods to UAE and Saudi ports (e.g., Jebel Ali, Dammam)
2. Middle Eastern Corridor:
- Modern rail network across Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Israel
- Digital and energy pipelines integrated along this route
3. Northern/European Corridor:
- Freight connectivity from Haifa Port (Israel) to Piraeus Port (Greece)
- Railway extension into Central and Western Europe (Germany, France, Italy)
⏳ Timeline of Developments
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 2021 | PGII launched by G7 nations |
| Sept 2023 | IMEC announced at G20 New Delhi Summit |
| 2024 | Feasibility studies and funding frameworks initiated |
| 2025–2030 | Expected phased construction and implementation |
📈 Economic and Strategic Objectives
- Reduce time and cost of trade between India, the Gulf, and Europe
- Diversify global supply chains and reduce overdependence on China
- Strengthen digital and energy cooperation
- Create jobs and investment opportunities in infrastructure, logistics, and services
- Promote economic integration across Asia, Middle East, and Europe
🌐 Geopolitical and Strategic Significance
- Counter to China’s BRI: Provides an alternative corridor based on transparency, sustainability, and rules-based governance
- Enhances India’s role as a key regional and global connector
- Deepens India–Middle East ties: Complements India’s outreach through I2U2 (India-Israel-UAE-USA)
- Increases EU’s strategic presence in Asia
- Boosts US engagement in global infrastructure diplomacy
🔬 Technological Integration
- Smart railways and ports with AI-powered logistics
- Blockchain-based cargo tracking
- Green hydrogen pipelines from Middle East to Europe
- Optical fiber and satellite-linked communication systems
- Digitally interoperable payment gateways and smart trade documentation
📊 Data and Trade Flow Potential
- Estimated to reduce shipping time by 40% between India and Europe
- Could handle trade worth $500–$800 billion annually by 2040
- India’s trade with EU (2022): ~$120 billion; projected to double by 2030
- Estimated to generate millions of jobs in logistics, construction, and digital sectors
🔍 Multidimensional Impact
💰 Economic:
- Lowers cost of freight and improves logistics efficiency
- Encourages manufacturing investments along corridor zones
- Connects key economic hubs and inland manufacturing clusters
🌱 Environmental:
- Promotes green shipping and rail over air freight
- Supports renewable energy grids and pipelines
🤝 Social:
- Facilitates people-to-people ties through cultural and academic exchanges
- Expands employment and skill development across nations
🛡️ Security:
- Reduces chokepoints like Suez Canal and Strait of Hormuz
- Enhances cyber-security cooperation through joint digital platforms
🧭 Political:
- Strengthens India's Act West policy
- Reinforces Europe–Middle East–Asia trilateral cooperation
- Increases the multipolarity of global trade governance
❗ Challenges and Bottlenecks
- Political instability in the Middle East
- Israel–Palestine conflict poses uncertainty to corridor continuity
- Need for massive financial and diplomatic coordination
- Bureaucratic bottlenecks in customs, visa, and security regimes
- Competition from BRI, INSTC, and other corridors
💡 Recommendations and Way Forward
- Establish an IMEC Secretariat for coordination
- Focus on public-private partnerships (PPP) for funding
- Align with SAGAR (India’s maritime vision) and Make in India
- Leverage multilateral institutions like World Bank, ADB, and AIIB for financing
- Create a cross-national digital customs and payment framework
- Promote green corridor certification and carbon-neutral targets
🔮 A Corridor of Dreams: Vision 2047
By India’s centenary of independence in 2047, IMEC could:
- Be the largest intercontinental trade spine
- Integrate digital economies, smart energy, and AI-driven logistics
- Serve as a model of inclusive, sustainable, and peaceful global development
🏁 Conclusion
“Infrastructure is diplomacy. Corridors are conversation. Trade is trust.”
The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor is not merely an economic pathway—it is a civilizational bridge that rekindles ancient trade routes with the power of modern innovation and diplomacy. As nations collaborate and invest in shared prosperity, IMEC may become a pillar of a new world order that values resilience, cooperation, and sustainability.